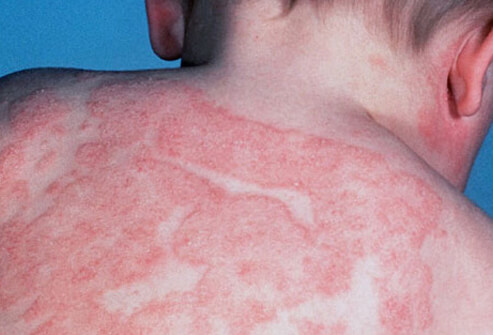
Eczema is a form of dermatitis, or inflammation of the epidermis. The term eczema is broadly applied to a range of persistent skin conditions. These include dryness and recurring skin rashes which are characterized by one or more of these symptoms: redness, skin edema (swelling), itching and dryness, crusting, flaking, blistering, cracking, oozing, or bleeding. Areas of temporary skin discoloration may appear and are sometimes due to healed lesions, although scarring is rare. In contrast to psoriasis, eczema is often likely to be found on the flexor aspect of joints.
ETIOLOGY
Predisposing causes are-
• Individual susceptibility to offending agent.
• Familial predisposition.
• Prolonged exposure to sunlight.
• Exposure to ultra-voilet rays.
• Trauma.
• Infection.
• Psychogenic stress.
• Pre-existing disease.
• Poor general health.
• Hyperhydrosis.
• Focal sepsis.
• Exposure to allergen.
• During hormonal immbalance.
• Sedentry life.
• Constipation.
• Any other condition which lowers local skin resistance.
Classification of Eczema / Dermatitis
The term eczema refers to a set of clinical characteristics. Classification of the underlying diseases has been haphazard and unsystematic, with many synonyms used to describe the same condition. A type of eczema may be described by location (e.g. hand eczema), by specific appearance (eczema craquele or discoid), or by possible cause (varicose eczema). Further adding to the confusion, many sources use the term eczema and the term for the most common type of eczema (atopic eczema) interchangeably.
The classification below is ordered by incidence frequency.
Types of common eczemas
Atopic eczema
Also known as infantile eczema, flexural eczema, atopic dermatitis. Atopic eczema is an allergic disease believed to have a hereditary component, and often runs in families whose members also have hay fever and asthma. Itchy rash is particularly noticeable on head and scalp, neck, inside of elbows, behind knees, and buttocks. Experts are urging doctors to be more vigilant in weeding out cases that are, in actuality, irritant contact dermatitis. It is very common in developed countries, and rising.
Contact dermatitis
C.D. is of two types: allergic (resulting from a delayed reaction to some allergen, such as poison ivy or nickel), and irritant (resulting from direct reaction to a detergent, such as sodium lauryl sulfate). Some substances act both as allergen and irritant (wet cement). Other substances cause a problem after sunlight exposure, bringing on phototoxic dermatitis. About three quarters of cases of contact eczema are of the irritant type, which is the most common occupational skin disease. Contact eczema is curable provided the offending substance can be avoided, and its traces removed from one’s environment.
Xerotic eczema
Also known as craquele or craquelatum, winter itch, pruritus hiemalis. X.E. is dry skin that becomes so serious it turns into eczema. It worsens in dry winter weather, and limbs and trunk are most often affected. The itchy, tender skin resembles a dry, cracked, river bed. This disorder is very common among the older population. Ichthyosis is a related disorder.
Seborrhoeic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis (“cradle cap” in infants) is a condition sometimes classified as a form of eczema which is closely related to dandruff. It causes dry or greasy peeling of the scalp, eyebrows, and face, and sometimes trunk. The condition is harmless except in severe cases of cradle cap. In newborns it causes a thick, yellow crusty scalp rash called cradle cap which seems related to lack of biotin, and is often curable.
Photodermatitis
Sensitisation of skin after exposure to sunlight or contact with substances having phototoxic or photoallergic effect, & characterised by smarting, burning & hyperpigmentation. Common in summers. Exposed parts usually extensor surfaces.
Common sites are face,neck, hands, forearms & feet.
Less common eczemas
Dyshidrosis
Also known as pompholyx, vesicular palmoplantar dermatitis, housewife’s eczema. Only occurs on palms, soles, and sides of fingers and toes. Tiny opaque bumps called vesicles, thickening, and cracks are accompanied by itching which gets worse at night. A common type of hand eczema, it worsens in warm weather.
Discoid eczema
It is characterized by round spots of oozing or dry rash, with clear boundaries, often on lower legs. It is usually worse in winter. Cause is unknown, and the condition tends to come and go.
Venous eczema
Also known as stasis dermatitis, varicose eczema. Occurs in people with impaired circulation, varicose veins and edema, and is particularly common in the ankle area of people over 50. There is redness, scaling, darkening of the skin and itching. The disorder predisposes to leg ulcers.
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Also known as Duhring’s Disease. Causes intensely itchy and typically symmetrical rash on arms, thighs, knees, and back. It is directly related to celiac disease and can often be put into remission with appropriate diet.
Neurodermatitis
Also known as lichen simplex chronicus, localized scratch dermatitis. It is an itchy area of thickened, pigmented eczema patch that results from habitual rubbing and scratching. Usually there is only one spot. Often curable through behavior modification and anti-inflammatory medication. Prurigo nodularis is a related disorder showing multiple lumps.
Autoeczematization
It is an eczematous reaction to an infection with parasites, fungi, bacteria or viruses. It is completely curable with the clearance of the original infection that caused it. The appearance varies depending on the cause. It always occurs some distance away from the original infection.