Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks the joints producing a inflammatory synovitis that often progresses to destruction of the articular cartilage and ankylosis of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can also produce diffuse inflammation in the lungs, pericardium, pleura, and sclera, and also nodular lesions, most common in subcutaneous tissue under the skin. Although the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown, autoimmunity plays a pivotal role in its chronicity and progression.
Cause of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
– Exact cause is not known.
– Evidence points to autoimmune etiology.
– Genetic predisposition common.
– Precipitating factors:
• Physical or emotional stress.
• After childbirth (remission during pregnancy)
– Hormonal disturbance:
• Puberty.
• Menopause.
– Age: 20 – 45 years
– Sex: common in females.
Pathogenesis: Joint deformity occurs in RA because the cartilage & then the bone is eroded by the proliferative synovial tissue. This process leads to increased laxity of ligaments around the joints, subluxation of tendons & subsequently of joints & inflammation of many other tissues in the body.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Prodorme
– Fatigue.
– Malaise.
Symptoms
– Joint stiffness more marked in morning.
– Pain in joints
– Limitation of movement of joints.
– Fever.
– Malaise.
– Night sweats.
– Loss of grip strength.
– Weight loss.
– Joint deformities.
Signs
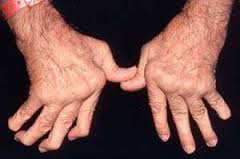
– Joints involved:
• Small joints.
• Bilaterally symmetrical.
• Joints swollen, hot & tender.
• Limitation of movements.– Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules present on extensor surfaces.
– Bursitis.
– Tenosynovitis.
– Muscle wasting above & below affected joints.
– Ulnar deviation of wrist.
– Swan neck deformity of fingers.
– Boutonniere deformity of fingers.
– Z-thumb deformity.
– Tender prominent metatarsal heads with secondary corns.
– Lateral deviation & over-riding of toes with pressure sores.
– Baker’s cyst: – Herniation of synovial cavity into back of knee causing pain & tenderness of calf.
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
1) X-Ray joint.
2) Synovial biopsy.
3) CBC.
4) Synovial fluid analysis.
5) Rheumatoid factor.
Complications of Rheumatoid Arthritis
– Subluxation of atlanto-axial joint.
– Carpal tunnel syndrome.
– Fibrosing alveolitis.
– Sjogren’s syndrome.
– Septic arthritis.
Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
– Bed rest.
– Well balanced, high protein, easily digestible diet.
– Local rest to joints with splints (to prevent deformity)
– Physiotherapy to avoid contractures.
– Local infra-red radiation or short wave diathermy for relaxation of muscles & relief of pain.